How to Change Directory in Ubuntu
The cd command is used for changing directories in Ubuntu command line. Here's how to use it.

So you have just started using the terminal and have no idea how to change the directory?
As always, Linux has a specific utility to change the directory named cd. And you can use it in this manner.
cd directory_name_or_pathIn this tutorial, I will show you how to use the cd command to change your current working directory.
Change the directory in Ubuntu
The cd command has various options that allow you to switch between various directories and here, I will walk you through some of the most useful ones.
But before I jump to the examples, here's a quick summary of the cd command with various options:
| Command | Description |
|---|---|
cd .. |
Switch back to the parent directory. |
cd ../../ |
Move two directories up to the current working directory. |
cd ~ |
Switch to the home directory. |
cd / |
Gets you into the root filesystem of Linux. |
cd - |
Switch to the previous working directory. |
cd /absolute/path |
Use the absolute path to change the directory. |
I hope you are familiar with the concept of paths in Linux. This will help you change the directories.
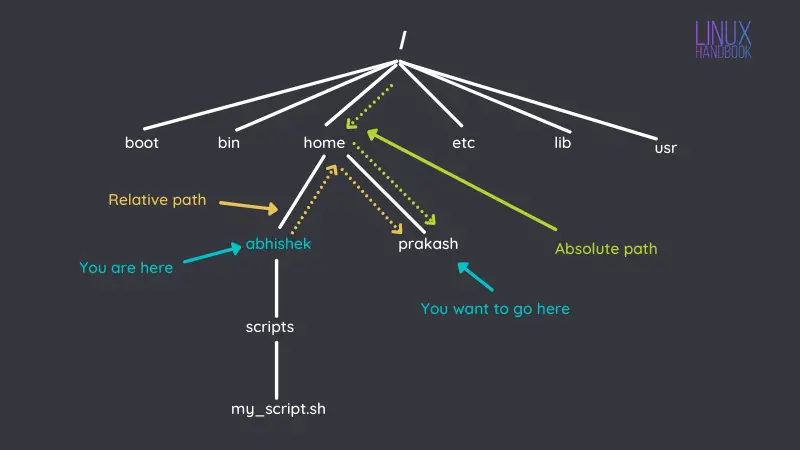
Switch back to the parent directory
To switch back to the parent directory, all you have to do is use the cd command in the following manner:
cd ..For example, here, my current working directory is /Downloads/aaa so if I want to switch back to the /Downloads directory, using cd .. will get the job done:
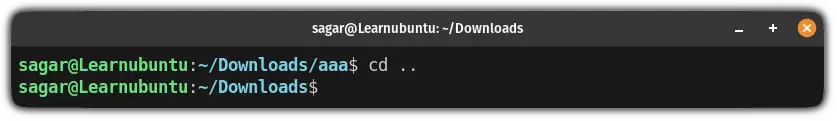
Move two directories up from the current working directory
In the above example, I explained how you can switch to one step above the current working directory. But what if you want to move two directories up?
In that case, all you have to do is use the following command:
cd ../../Here, I'm inside /etc/pop-os/flatpak directory and I want to switch to the /etc (moving two directories up):
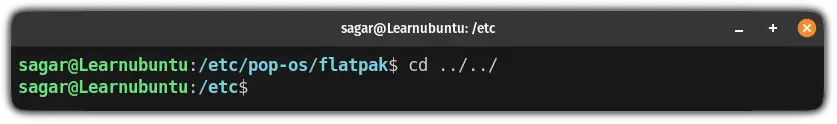
Switch to the home directory
So if you want to switch to the home directory, all you have to do is append the ~ following by space to the cd command:
cd ~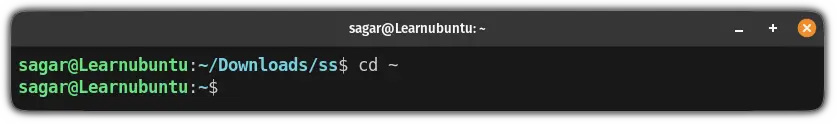
And as you can see, by executing cd ~ I was immediately thrown into the home directory.
Get into the root filesystem of the Linux
Want to get into the root filesystem? All you have to do is append the forward slash / with single space to the cd command:
cd /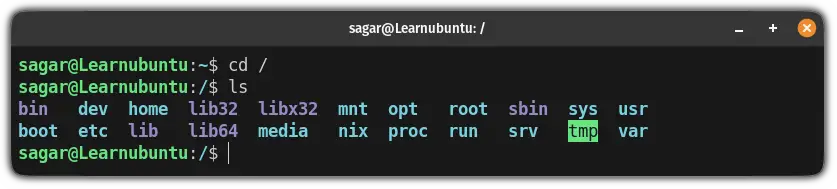
Switch to the previous working directory
Suppose you are working on a file inside the Downloads directory but all of a sudden, you have to make a few changes to the root filesystem.
Once done, you need to go back to your previous working directory. So what option do you have in that case?
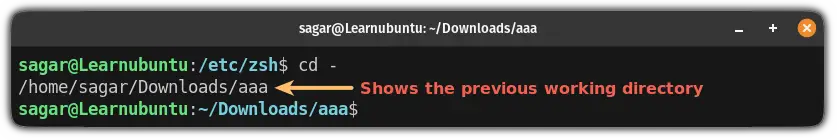
Simple! Use the cd command in the following manner:
cd -In my case, I was working on /Downloads/aaa and later on, I had to switch to /etc/zsh so here, I used cd - to go back to the /Downloads/aaa:
Change the directory with the absolute path
If you know the absolute path to the directory, you can jump to the desired directory from any place.
To know the absolute path of the current working directory, you can use the pwd command:
pwd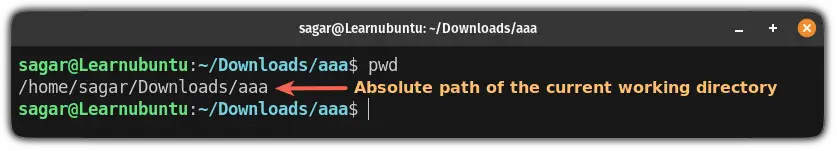
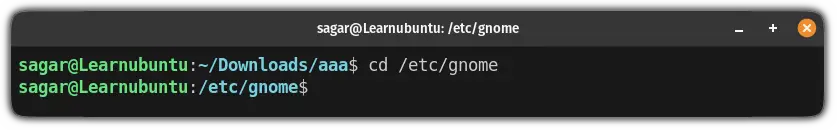
Once you are familiar with the absolute path, all you have to do is append the absolute path to the cd command:
cd /absolute/path/to/directoryFor example, here, I changed my directory from /Downloads/aaa to the /etc/gnome:
A pretty neat way of switching back and forth. Isn't it?
Want to learn bash from scratch? I got you!
Using a shell script, you can unlock the true potential of Linux, so how about learning it from scratch?
And if you want to do so, we have a dedicated series for you:

I hope you will find this guide helpful. And if you have any queries, feel free to ask in the comments.
A software engineer who loves to tinker with hardware till it gets crashed. While reviving my crashed system, you can find me reading literature, manga, or watering my plants.

