How to Check File Permissions in Ubuntu
Here's how to check file permissions in Ubuntu command line.

So you were on your way to executing a file and suddenly got an error saying "Permission denied"

In that case, the chances of you were not allowed to access the file are pretty high.
The usual way to see the file permission is to use the long listing option with ls command:
ls -l filenameBut you need to understand the concept of file permission and ownership to actually understand its meaning.
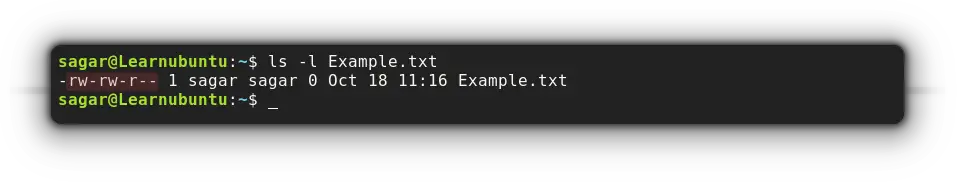
Another way check the file permission in ubuntu is to use the getfacl utility:
getfacl filename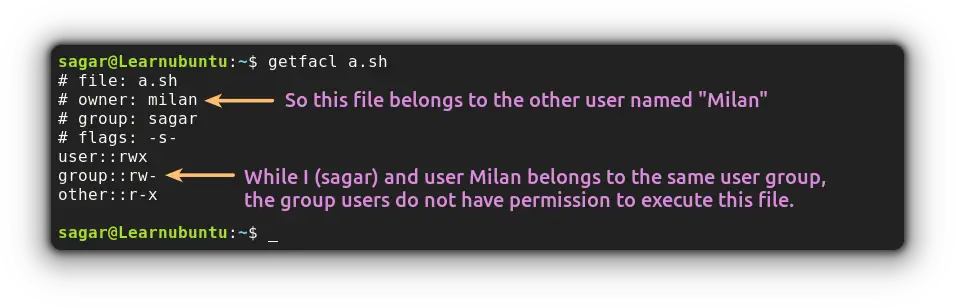
There are other methods to check file permissions but before that, let's understand file permission in Linux.
Understanding file permissions in Ubuntu
Linux by its nature gives the ability to have multiple users in a single system and that came with the threat as any other user can access your sensitive documents.
And this is where the file permissions come to save you.
So there are 3 types of ownership in Linux:
- User ownership.
- Group ownership.
- Others.
While there are 3 types of permission in Linux:
- Read (r).
- Write (w).
- Execute (x).
For better understanding, let's take an example of the ls command:

So you get a sequence of permission but how you are supposed to know which is for the user and which is for group users? Well, here's the illustration:
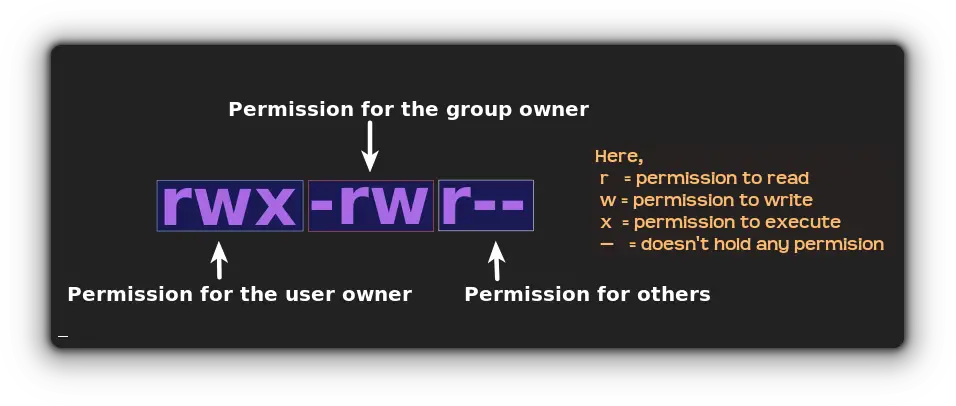
So now you know the basics, let's have a look at multiple methods by which you can check file permissions.
Check file permission in Ubuntu
In this guide, I'm going to share 3 ways by which you can check for file permissions in Linux. So let's start with the widely used one.
Using the ls command
The ls command is generally used to list files in a specific directory but you can also use it to get additional info such as file permissions.
To check file permissions using, you'd need to pair the ls command with the -l option.
ls -l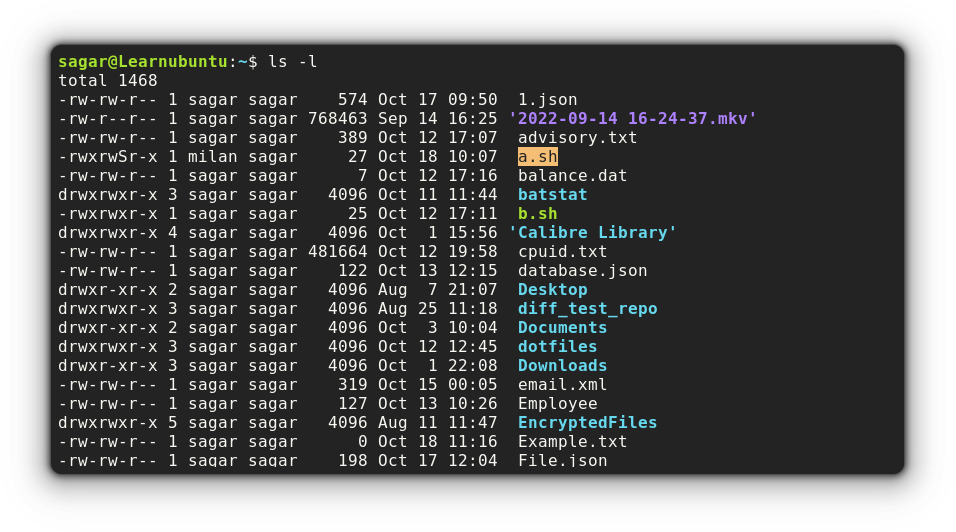
Similarly, you can also use -a option to show hidden files:
ls -la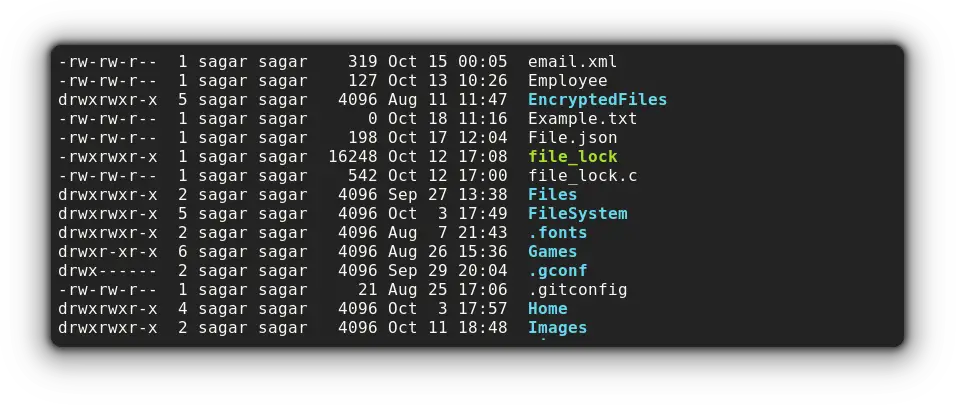
And if you want to know what each element in the above output stands for, I'd recommend checking the other guide of ours:

Using stat command
While the ls command gave me the list of files with read-write permission attached to each one, the stat command requires a file name as it gets even more details than the ls command.
To list file details, you just have to pair the filename with the stat command:
stat a.sh 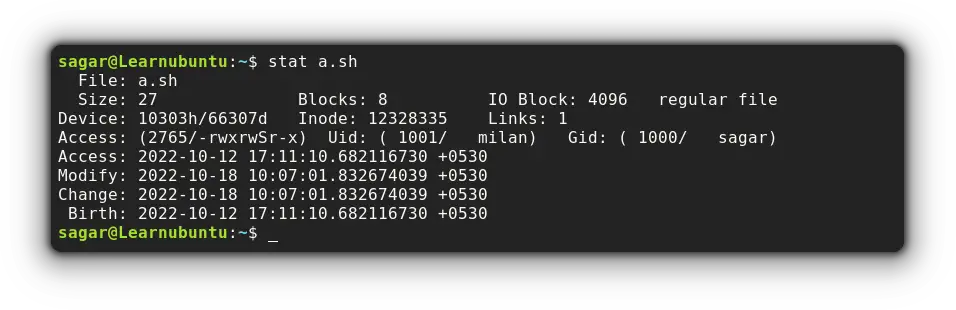
But if you are someone like me who prefers only necessary details, the stat command allows users to modify the output with the --format option:
stat --format "R/W/E permissions: %A, Group owner: %G, User owner: %U" a.sh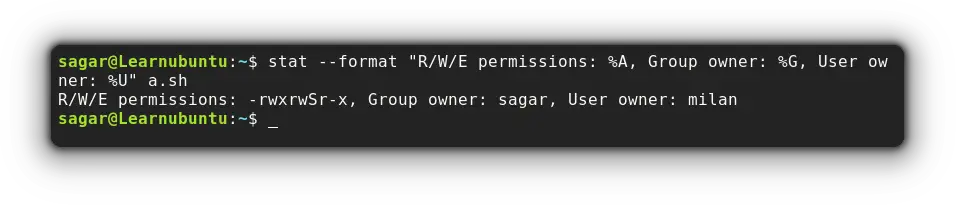
Here, I've used 3 variables with text attached to them making them more relevant:
%Ashows file permission.%Ggets the name of the group owner.%Uwill show the user owner.
Using the getfacl utility
This is my favorite utility when it comes to checking file permissions in Linux. And it comes pre-installed in Ubuntu too!
The reason why it is my favorite is that it only shows the necessary details and conveniently presents details.
Pair the filename with the getfacl utility and that's it:
getfacl filename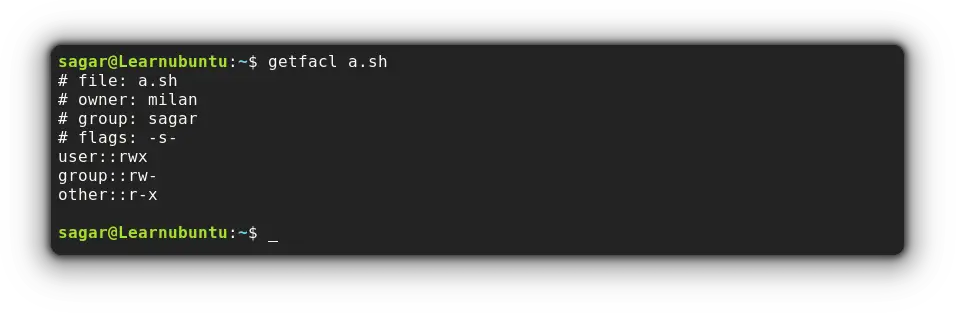
Wrapping Up
This was my take on how you can check file permissions in Ubuntu with some basics. And if you want to know how change the permission, use the chmod command.

A software engineer who loves to tinker with hardware till it gets crashed. While reviving my crashed system, you can find me reading literature, manga, or watering my plants.

