Set Date in Ubuntu Command Line
In some rare cases, you may want to set a different time and date in Ubuntu command line. Here's how to do that.

While installation, your system will get the correct time using the network and if you went with the offline installation, there's a hardware clock to get things done.
But if I'm writing this guide, it simply means there would be some situations when you want to set or change a date in Ubuntu.
So before we jump to the how-to part, let's have a look at why would one want to set the date in Ubuntu or any other Linux distribution.
Reasons to change date in Ubuntu
Here are some of the practical reasons why would one want to change or set the date in Ubuntu:
- The server's clock is out of sync with other computers on the network
- The clock was misconfigured during the installation
- Daylight saving is enabled and it needs to be tuned when it starts or ends
- The server was moved to a different place
It is possible that you may not find yours here and that's absolutely fine!
Now, let's have a look at multiple methods to set a date in Ubuntu.
How to set a date in Ubuntu
In this tutorial, I will share two different methods to set the date in Ubuntu:
- Using the date command
- Using the timedatectl command
But before you jump to any of the shown methods, it is important to disable the NTP in Ubuntu as if enabled, it won't let you change the date and time manually.
Disable NTP before changing the date in Ubuntu
In almost every Linux distribution, NTP (Network Time Protocol) is enabled by default and there's a strong reason why.
The NTP is used to synchronize the date and time of hosts and clients across the network without any intervention of humans.
But if you want to change the time manually, it won't let you do so and give you the following error (if you use the timedatectl command):
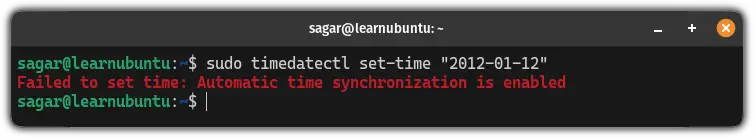
And if you use the date command for the same without disabling NTP, it won't change the date and time at all!
So first let's check whether it is enabled in your system using the timedatectl command:
timedatectl 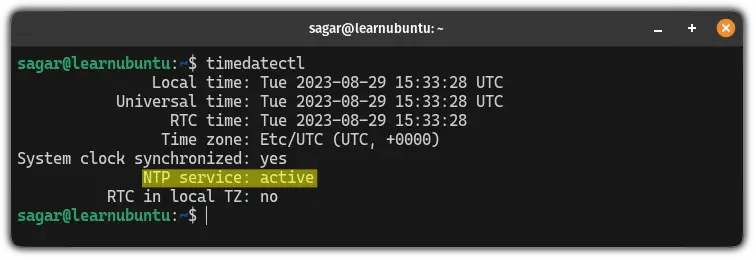
If it is enabled, use the following command to disable the NTP:
sudo timedatectl set-ntp false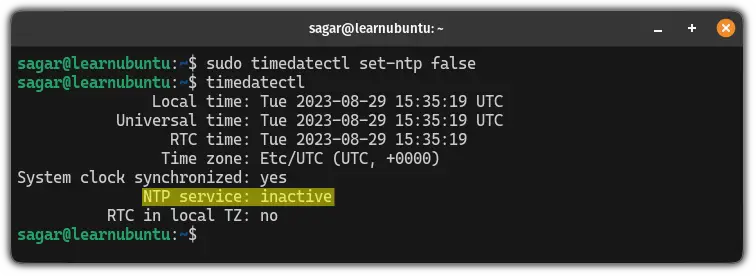
Now, let's have a look at multiple methods to change the date and time in Ubuntu.
1. Using the date command
The date command is generally used to know the current date and time in the system but can also be used to change the date and time when executed in the following manner:
sudo date --set="YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss"For example, here, I changed my current date to 30th Dec 2022 and time to 12:30:
sudo date --set="2022-12-30 12:30:00"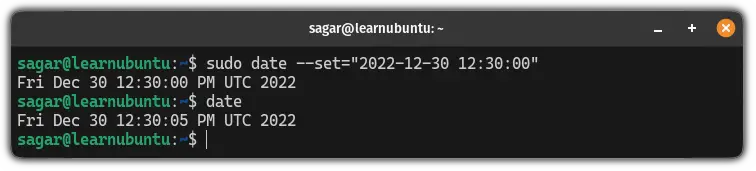
As you can see, when I used the date command to verify the current date and time, it showed as I configured.
2. Using the timedatectl command
The timedatectl command is a one-stop solution for all the date and time-related issues so it is a no-brainer that it can be used to change the date as well.
To change the date and time using the timedatectl command, use the following syntax:
sudo timedatectl set-time "YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss"For example, here, I changed my system time to 12th Jan 2012 and this time I won't specify the time so by default it will show 12:00:00:
sudo timedatectl set-time "2012-01-12"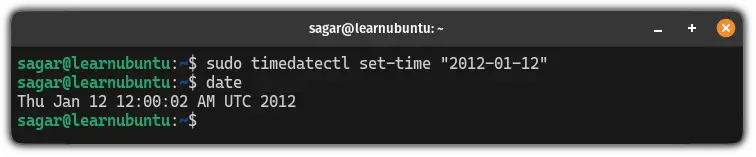
How to reset date and time to default in Ubuntu
If you want to go back to the default time, all you have to do is enable the NTP in Ubuntu and it will take care of the rest:
sudo timedatectl set-ntp true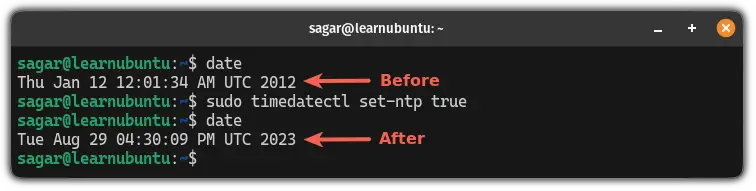
Final words
In this tutorial, I went through how you can set the date and time in Ubuntu with multiple methods and how to go back to the default settings.
You may also want to know about changing timezone in Ubuntu.

I hope changing date in Ubuntu is no longer complex task for you.
A software engineer who loves to tinker with hardware till it gets crashed. While reviving my crashed system, you can find me reading literature, manga, or watering my plants.

