How to Run Java Programs in Ubuntu Terminal
Here's a step by step that shows how you can run a Java program in the command line in Ubuntu.

If you are new to Linux and have no idea how to set up your system so you can code in Java, then this tutorial is just for you.
To run Java programs in Ubuntu command line, you have to follow 3 simple steps:
- Install java compiler
- Compile Java code
- Run compiled code
Let's start with the installation of the Java compiler.
Step 1: Install the Java compiler
Unlike modern programming languages like Python, in Java, every program must be compiled (the approach is similar to running C programs in Ubuntu).
The first step is to check if you already have it installed or not using the following command:
javac --version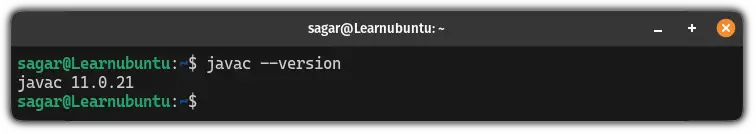
But if it throws you an error, it simply means the Java compiler is not installed and you have to install it manually.
The Java compiler is a part of the JDK (Java Development Kit) which means you need to install the JDK in Ubuntu to get the Java compiler.
To install JDK in Ubuntu, use the following command:
sudo apt install default-jdkStep 2: Compile the Java program
Once you have the compiler installed, let's have a look at how you can compile a program.
I will be using a simple Hello World:
public class Hello {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}
To compile a Java program, you'd have to use the javac command in the following manner:
javac Filename.javaI will be using the Hello.java file, so my command would look like this:
javac Hello.javaAfter the successful compilation, it will create a class file which is our compiled file and can be found by listing the contents of a directory:
ls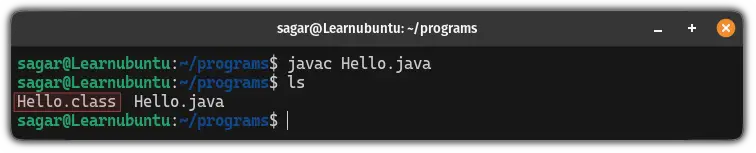
Step 3: Run the compiled Java program
Once you are done with the compilation, finally, you can run the Java file.
To run the compiled Java program, use the Java command along with the class file name (without using the .class extension):
java FilenameYep, you don't have to specify the .class extension after the filename!
In my case, it looked like this:
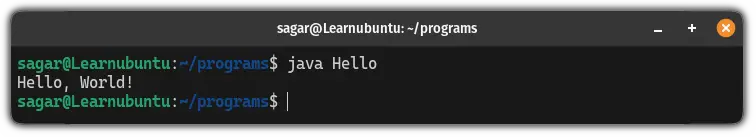
There you have it!
Running Java in modern IDEs? Setup JAVA_HOME Variable
If you are running Java programs in modern IDEs like Eclipse, Netbeans, Maven, etc. then it will require you to set up the JAVA_HOME variable.
Want to know how you do it? Here's a detailed guide explaining how to set JAVA_HOME variable in Ubuntu:

Have more queries? Leave a comment.
A software engineer who loves to tinker with hardware till it gets crashed. While reviving my crashed system, you can find me reading literature, manga, or watering my plants.

